Xeno-free Hydrogel for Xenograft
In Vivo Applications
Xeno-free Hydrogel for PDX and CDX
- Easy operation, smooth injection
- Homogenous cell suspension prior to injection
- Excellent cell retention after injection
- Fast cell growth kinetics
- Minimize operation error in each testing group
- Lot-to-lot batch consistency
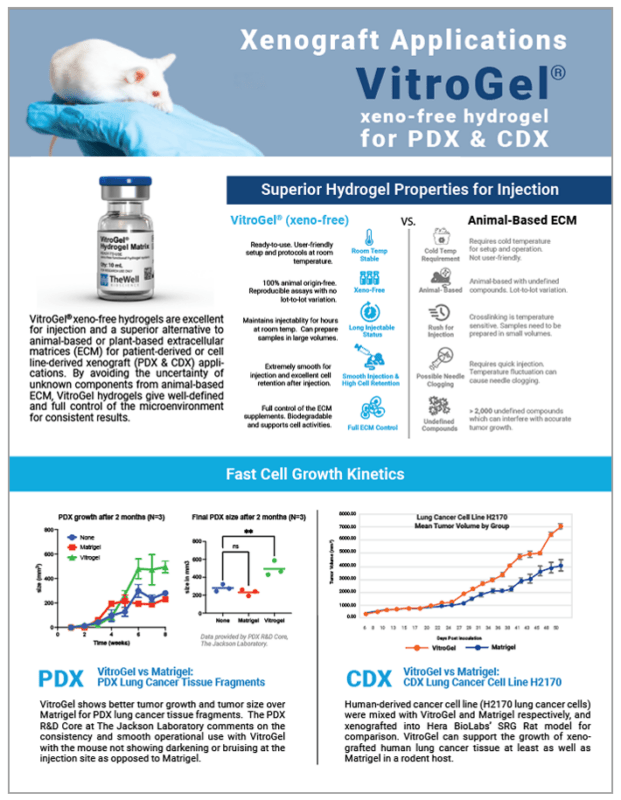
VitroGel® hydrogels are xeno-free (animal-free) and are excellent for injection and a superior alternative to the animal-based extracellular matrix (ECM) for patient-derived or cell-derived xenograft (PDX & CDX) applications. By avoiding the uncertainty of unknown components from the animal-based ECM, VitroGel® hydrogels give well-defined and full control of the microenvironment for consistent results.
The stable room temperature properties of VitroGel® makes it extremely smooth to work with for sample preparation and injection. Researchers have operational assurance and peace of mind with the long-term injectable status and the worry-free issue of possible needle clogging. After injection, the high cell retention rate ensures a rapid cell growth rate with a consistent, smooth/round tumor shape.
Simply Replace Animal-Based ECM With VitroGel® & Enjoy These Benefits
simple protocol - extremely smooth usability
VitroGel® hydrogel injection Protocol Video Demonstration
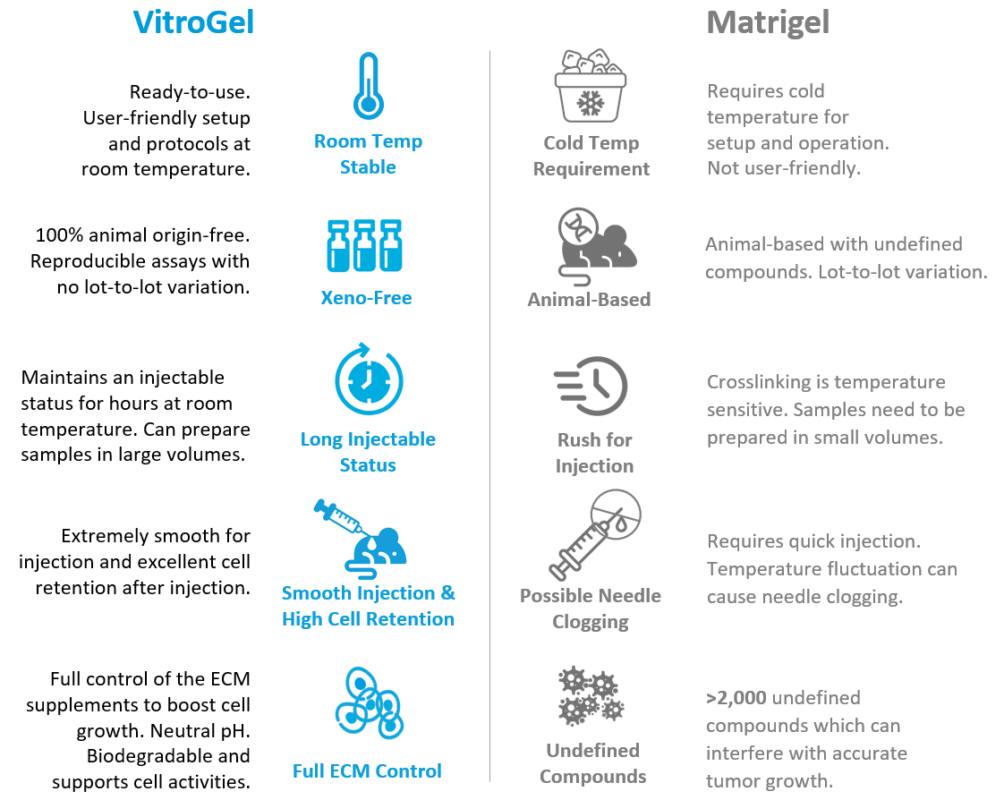
- VitroGel® is room temperature stable with a neutral pH, unlike animal-based extracellular matrix.
- Researchers do not need to worry about putting the solution on ice, the fast gel crosslinking, or the rush for injection.
- VitroGel® has a unique rheological property that can maintain an excellent injectable status for hours after mixing with cells.
UNIQUE RHEOLOGICAL PROPERTIES FOR LONG-TERM INJECTABILITY
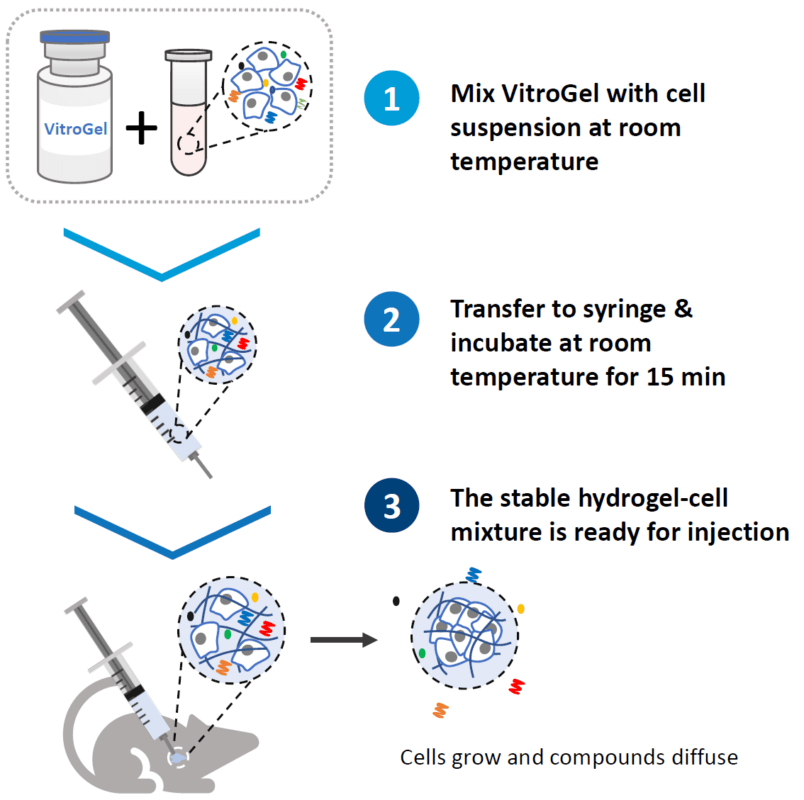
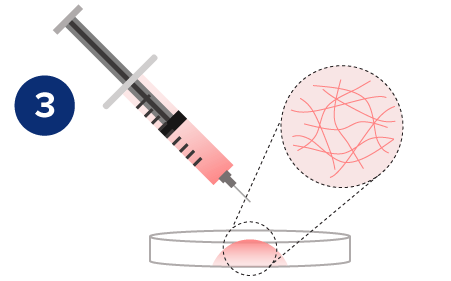
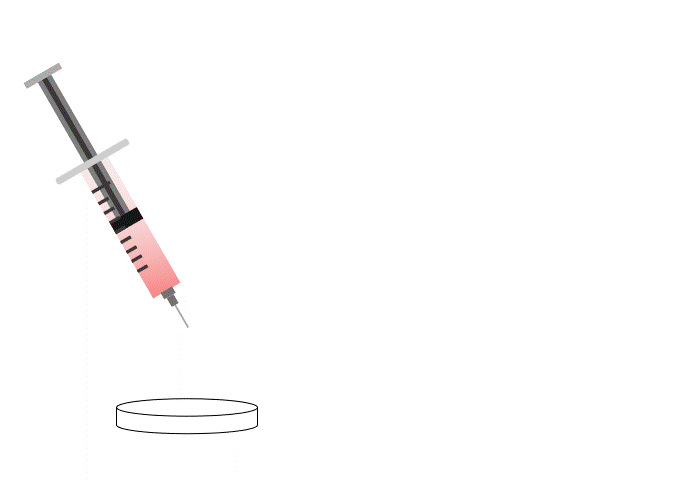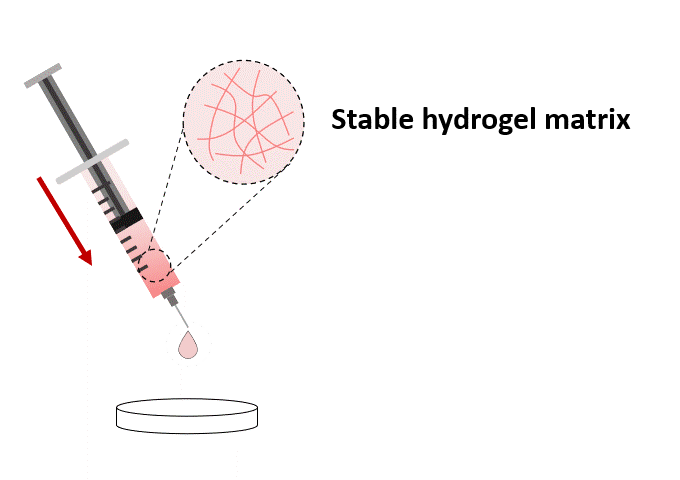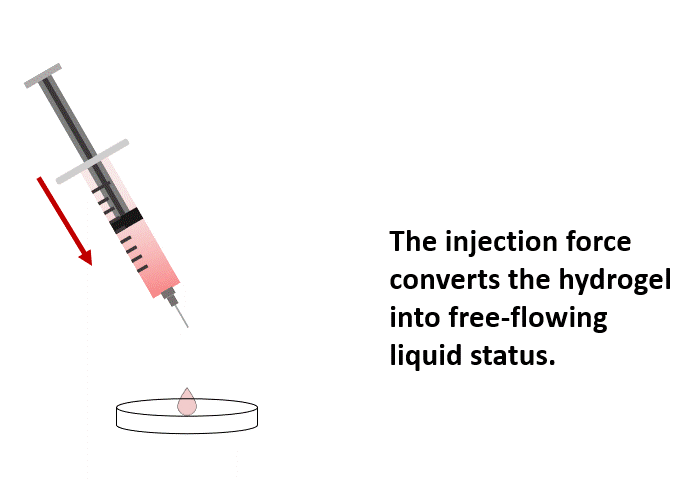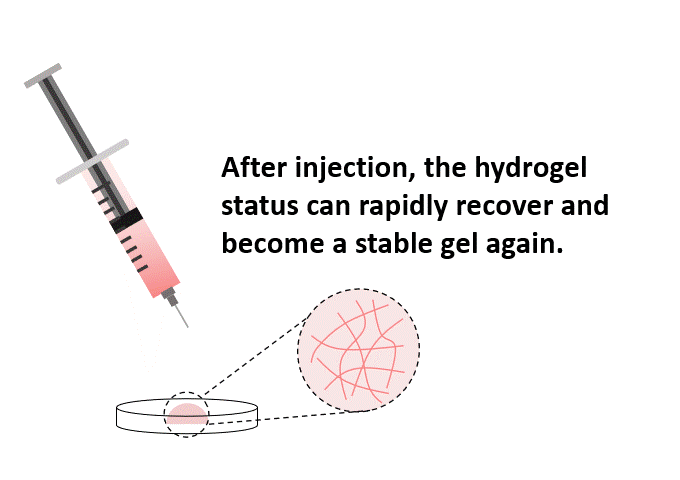
Once mixed with the cell suspension, (1) the stable hydrogel mixture maintains a long injectable status. (2) Under the mechanical shearing force, such as injection through a syringe, the soft hydrogel performs a gel-sol transition and becomes free-flowing status. However, once the shearing force ceases, (3) the mechanical strength of the hydrogel can rapidly recover with a sol-gel transition and become a hydrogel status again. With this unique injectable property, cells or compounds can be pre-mixed with VitroGel® solution and maintained as a homogeneous mixture in the injectable state for in vivo applications.
Stable Soft Hydrogel
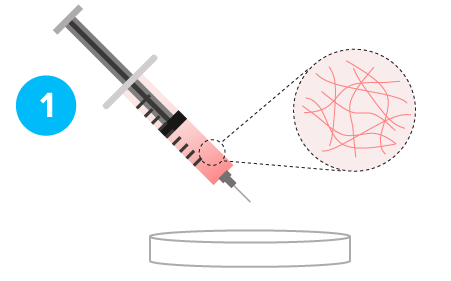
Gel-Sol Transition
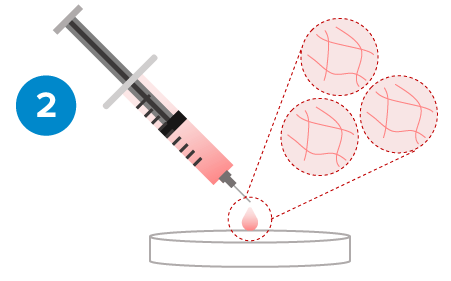
Rapid Hydrogel Recovery
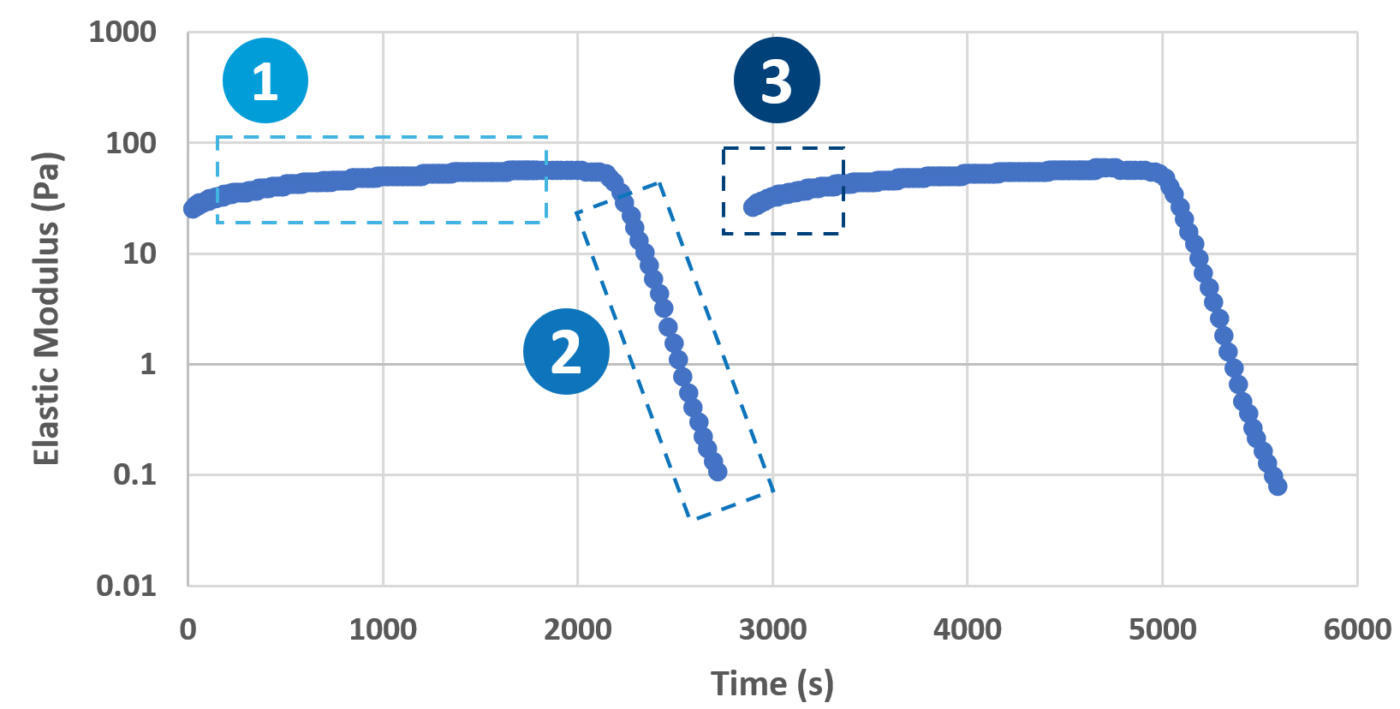
The rheological data shows the shear-thinning and rapid rheological property of VitroGel®
Assured biocompatibility
VitroGel® is biocompatible without toxicity

Hydrogel is stable after injection. The material is biocompatible without toxicity.
“The VitroGel® worked extremely well and was very smooth to work with as opposed to the Matrigel. Upon observation today, the “tumor only” and “tumor and Matrigel” mice appear to have darkening and bruising at the injection site, whereas the “tumor and VitroGel®” and “tumor, VitroGel® and cisplatin” do not have any darkening or bruising at the injection sites.”
VitroGel® passed pathogen testing with negative results.
The hydrogel is biocompatible without any sign of toxicity
After 8 weeks of in vivo incubation, there was no inflammatory response.
xenograft faq
Most customers working with mice use an injection volume of 100-200 μL (depending on cell type). For rat models, the injection volume is about 500 μL.
The typical implanting cell number is between 1 to 10 x 106, depending on different cell types. The cell suspension can be prepared in PBS to obtain 2-20 x 107 cells per mL and then be mixed with VitroGel® at 1:1 ratio (v/v). The cell density can be adjusted based on the inoculation volume (e.g., 100 or 200 μL) as well as the mixing ratio between VitroGel®: Cell suspension. Please check user protocols for different mixing ratios.
No. Unlike Matrigel, VitroGel® is ready-to-use and can mix with a cell suspension at room temperature. After the hydrogel and cell suspension are mixed and transferred to a syringe, you can put the mixture on ice, or 4°C, for 5-10 minutes to accelerate the injectable hydrogel formation and ensure a homogenous cell suspension. After that, the hydrogel can be kept at room temperature for long-term injection. Alternately, if you don’t want to use cold temperature for any part of the protocol, simply put the hydrogel-cell mixture at room temperature for 15 minutes for gel stabilization before injection. VitroGel® has a unique shear-thinning and rapid recovery property, which can maintain a long-term injectable status (hours) and excellent cell retention after injection without the needle clogging issue (Please check this page for more details and illustrated protocol).
As opposed to Matrigel, which has a fast solidification process when the temperature is higher than 10 degrees Celsius, the VitroGel-Cell mixture forms a soft injectable hydrogel. The hydrogel has a unique shear-thinning and rapid recovery property which enables it to retain its injectable status for months even (unless more culture is not added or for as long as the cells survive).
After injection, the sol-gel transition happens immediately, which rebuilds the mechanical strength of the hydrogel and holds cells within the hydrogel matrix. Hence, our hydrogel system has excellent cell retention after injection.
No. Adding supplements to the hydrogel matrix is not required. For most xenograft applications, preparing cells in PBS solution works extremely well with VitroGel®. On the other hand, VitroGel® is animal-origin free, which gives the flexibility for researchers to manipulate the supplement in a gel-cell mixture if needed.
The growth factors added depend on your application and system. The common ones include BSA, HSA, serum replacement, etc. If serum supplement is not a concern, you can also add FBS to give the system an extra push to see promising cell growth.
No, there is no issue with bubble formation due to the low viscosity of VitroGel®. There is an option to warm the medium and hydrogel solution before mixing them, as this can help reduce the viscosity.
Yes, VitroGel® allows for different injection sites like subcutaneous, orthotopic, IP, etc. Some injections that are difficult with an animal-based matrix perform smoother with VitroGel®.
VitroGel® performs extremely well for tumor formation. The tumor formation rate is almost 100% for typical cell types and even over 70% for some difficult cell types. In most cell types, the tumor growth kinetics in VitroGel® are faster or equal to Matrigel.
Fast CELL GROWTH KINETICS
CDX:
This application note specifically details the comparison between using a widely popular animal-based ECM versus VitroGel® in CDX mouse models to study tumor characteristics. Some of the most widely used cell types in CDX models were chosen for this study, including prostate (PC3), cervical (HeLa), breast (HCC1806), colon (HCT116), lung (Calu-6), and pancreas (PANC1).
Read the Application Note
CDX:
Two human-derived cancer cell lines (H2170 lung cancer cells and PC3 prostate cancer cells) were mixed with VitroGel® and Matrigel, respectively, and xenografted into Hera BioLabs’ SRG Rat model for comparison. The results show that VitroGel® supports faster or equal cell growth kinetics compared to Matrigel. Data provided by Hera BioLabs.
Read the white paperPDX:
VitroGel® shows better tumor growth and tumor size over Matrigel for PDX lung cancer tissue fragments. The PDX R&D Core at the Jackson Laboratory comments on the consistency and smooth operational use with VitroGel®, in addition to the mouse not showing darkening or bruising at the injection site as opposed to Matrigel.
Data provided by PDX R&D Core, The Jackson Laboratory.
Excellent for drug discoveries
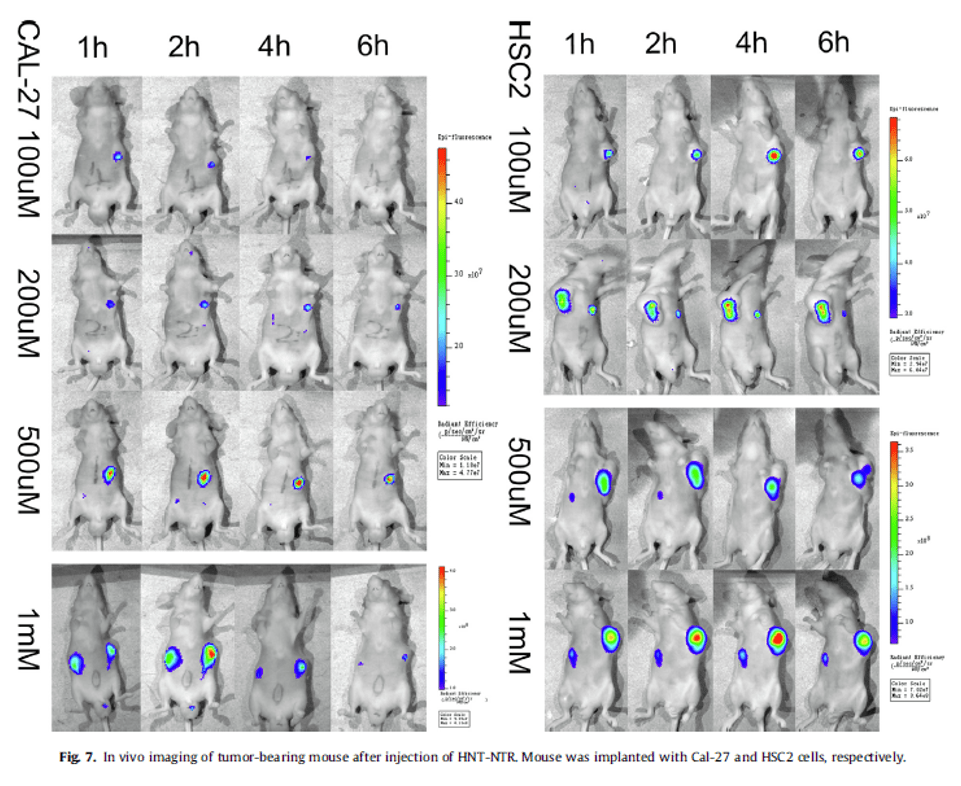
Ultra-sensitive responsive near-infrared fluorescent nitroreductase probe with strong specificity for imaging tumor and detecting the invasiveness of tumor cells
Ref. Spectrochimica Acta Part A, 268, 120634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120634
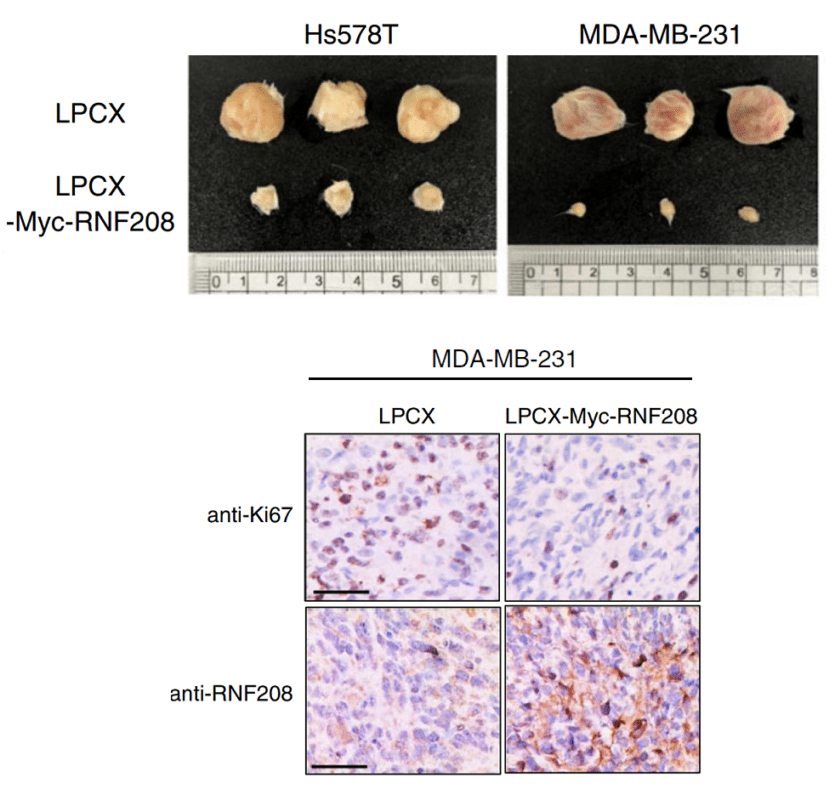
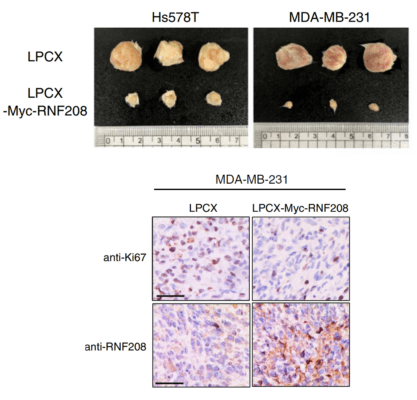
RNF208, an estrogen-inducible E3 ligase, targets soluble Vimentin to suppress metastasis in triple-negative breast cancers
Ref. Nature Communications, 10(1), 5805. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13852-5
SUPPORT A WIDE RANGE OF CELL TYPES WITH HIGH TUMOR FORMATION RATE
| Breast | Hs578T | VHM01, TWG003 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous | 10 million | 20 mm | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | VHM01 | NSG Mouse | Subcutaneous (right flank) | 10 million | 1500-2000 mm3 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | VHM01, TWG003 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous and Tail vein | 10 million | 20 mm | |||
| HCC1806 | VHM01 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous (dorsal thigh) | 10 million | 2000 mm3 | |||
| Cervical | HeLa | VHM01 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous (dorsal thigh) | 1 million | 400 mm3 | ||
| SiHa (HPV+) | VHM01 | Nude Mice | Subcutaneous injection | 2.5 million | 15 mm | |||
| Colon | HCT-116 | VHM01 | NSG Mouse | Subcutaneous (right flank) | 1-10 million | 850-2800 mm3 | ||
| HCT-116 | VHM01 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous (dorsal thigh) | 10 million | 2000 mm3 | |||
| Fibrosarcoma | HT1080 | VHM01 | SRG Rat | Subcutaneous (dorsal hind flank) | 2.5 million | 30-40 mm | ||
| Glioma | U87-MG | VHM01 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous (dorsal thigh) | 10 million | 2000 mm3 | ||
| Kidney | 786-O | VHM01 | SRG Rat | Subcutaneous (dorsal hind flank) | 5 million | 25 mm | ||
| Leukemia | CCRF-CEM | VHM01 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous (dorsal thigh) | 5 million | 2000 mm3 | ||
| Lung | A549 | VHM01 | NSG Mouse | Subcutaneous (right flank) | 10 million | 1900-2400 mm3 | ||
| PDX Lung Cancer Tissue Fragments | VHM01 | NSG Mouse | Subcutaneous | fragments | 500+ mm3 | |||
| Calu-6 | VHM01 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous (dorsal thigh) | 10 million | 2000 mm3 | |||
| H2170 | VHM01 | SRG Rat | Subcutaneous | 10 million | 30-40 mm | |||
| LLC-OVA | VHM01 | WT B6 Mouse | Subcutaneous injection (left flank) | 500,000 | 14 mm | |||
| Melanoma | A375 | VHM01 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous (dorsal thigh) | 5 million | 2000 mm3 | ||
| B16-OVA MO4 Mouse Melanoma Cells | VHM01 | Mouse | Subcutaneous injection | 150,000 | (low cell # injection) | 5-7 mm | ||
| B16-OVA MO4 Mouse Melanoma Cells | VHM01 | Mouse | Subcutaneous injection | 150,000 | (low cell # injection) | 5-7 mm | ||
| Neuroblastoma | Neuroblastoma PDX cells | VHM01 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous injection | 10 million | 300 mm3 | ||
| BE2C | VHM01 | NOD-SCID Mice | Subcutaneous injection | 1 million | 10-15 mm | |||
| Oral | HSC-2 | VHM01 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous | 1.5 million | 10-15 mm | ||
| Pancreas | ASPC-1 | VHM01 | NSG Mouse | Subcutaneous (right flank) | 10 million | 900-1700 mm3 | ||
| PANC1 | VHM01 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous (dorsal thigh) | 10 million | 400 mm3 | |||
| Prostate | Mouse Prostate Cancer Cells | VHM01 | Mouse | Subcutaneous injection | 1 million | 5-7 mm | ||
| A549 | VHM01 | NSG Mouse | Subcutaneous (right flank) | 10 million | 1900-2400 mm3 | |||
| PC3 | VHM01 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous (dorsal thigh) | 2 million | 1000 mm3 | |||
| PC3 | VHM01 | SRG Rat | Subcutaneous (dorsal hind flank) | 5 million | 30-40 mm | |||
| Tongue | CAL-27 | VHM01 | Nude Mouse | Subcutaneous | 10 million | 15-25 mm |
*The data above is based on internal studies and customer feedback.
VHM01=VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix | TWG003=VitroGel® RGD | VHM04-4=VitroGel® ORGANOID-4
The list is constantly growing. Please contact support if you do not see a cell type of interest listed – support@thewellbio.com
View tables of cells cultured in vitro with VitroGel®: Cell Type Hydrogel Guide
Selecting the functional hydrogel for your xenograft project
All VitroGel® hydrogels are injectable and excellent for xenografts.
While we offer a repertoire of hydrogels, both ready-to-use, and tunable high-concentration hydrogels for xenograft, we recommend starting with VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix as it is widely used for xenograft applications.
VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix supports a wide variety of cell types including many cancer cells, epithelial cells, stromal cells, and primary cells. Great for cells needing strong cell-matrix interactions.
Below are some more hydrogel recommendations based on the popular applications:
Our xeno-free functional hydrogel system is designed based on the application needs (Ready-To-Use VitroGel®) and the biochemical/biophysical properties needs (High Concentration VitroGel®). Researchers have full control of the supplement/growth factors in the hydrogel-cell mixture. Scientists can choose the hydrogels that fit their research objectives.
> Ready-To-Use VitroGel®
The ready-to-use VitroGel® hydrogels have optimized formulations of multi-functional ligands and concentrations. Each hydrogel is ready to mix directly with cells/compound suspension, offering an excellent balance of simplicity and versatility.
- VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix: Supports a wide variety of cell types, including many cancer cells, epithelial cells, stromal cells, and primary cells. Great for cells needing strong cell-matrix interactions. (VHM01)
- VitroGel® ORGANOID-4: Supports tumor organoid growth and is great for in vivo cell expansion. (VHM04-4)
> High Concentration VitroGel®
The high-concentration hydrogels allow the flexibility to manipulate the mechanical strength of the hydrogel (tunable) by adjusting the hydrogel concentration with the VitroGel® Dilution Solution. Each high-concentration hydrogel has a functional ligand modification, allowing scientists to investigate the cell behaviors with complete control of hydrogel properties.
- VitroGel® RGD: One of the most popular hydrogels for multiple in vivo applications. Supports a wide range of cell types with excellent cell-matrix interactions. Great for multiple cell therapy applications. (TWG003)
- VitroGel® MMP: Great hydrogel degradability to support rapid cell expansion and invasion/migration. Excellent for tumor study and xenograft. (TWG010)
- VitroGel® 3D: Pure hydrogel matrix without binding ligand modification. Great for simple target delivery and control release. (TWG001)
Case Studies/Research Highlights
ON-DEMAND WEBINAR
Join Dr. John Huang from TheWell Bioscience and Dr. Minqu Huang from HD Biosciences, a Wuxi AppTec company, to discuss VitroGel®, an animal-free hydrogel with superior injection properties and advantages over animal-based ECM for a more consistent xenograft.
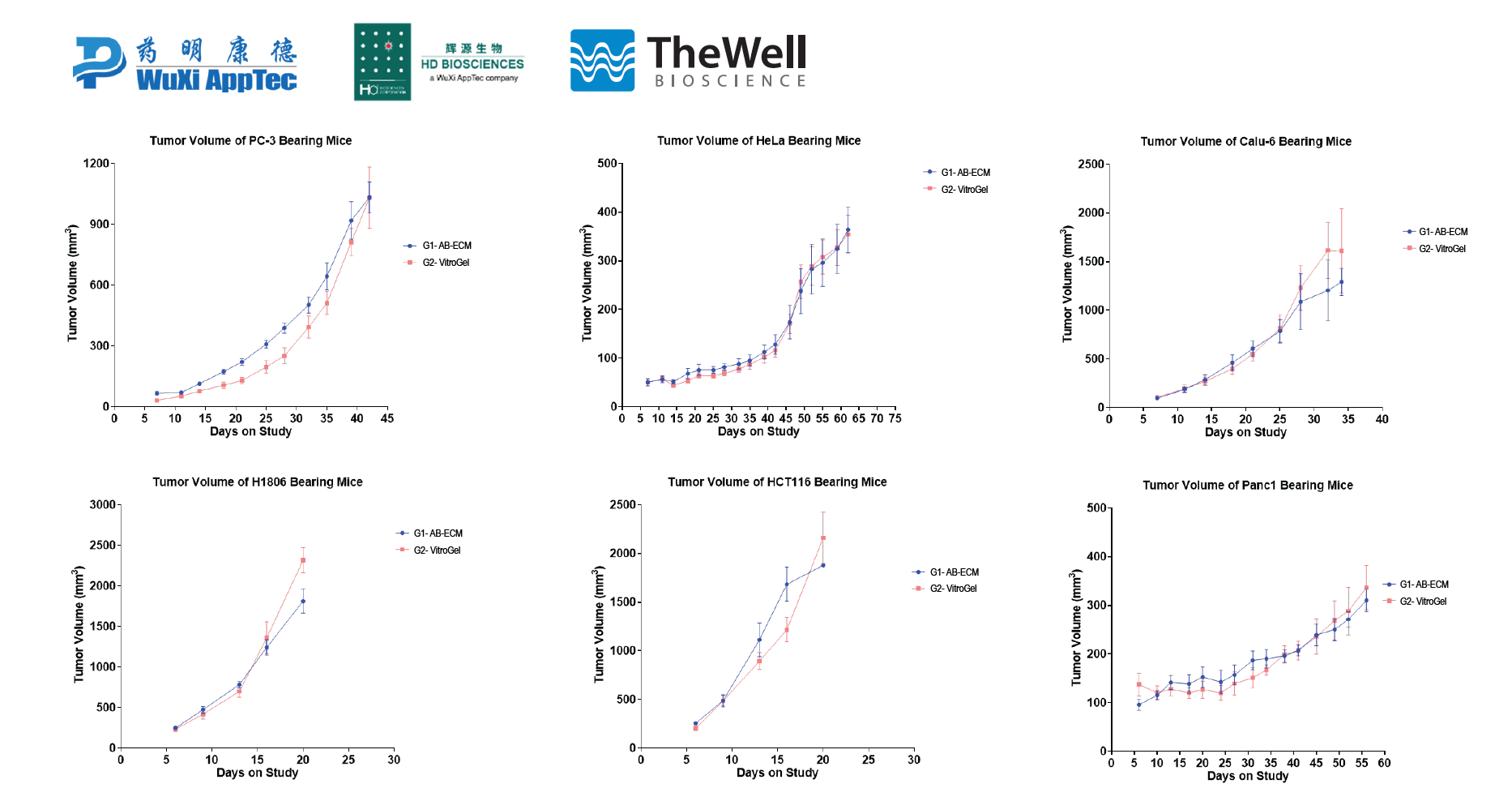
Cell Line-Derived Xenograft Using Xeno-free VitroGel® System in Comparison to Animal-based Extracellular Matrix
This application note specifically details the comparison between using a widely popular animal-based ECM versus VitroGel® in CDX mouse models to study tumor characteristics. Some of the most widely used cell types in CDX models were chosen for this study, including prostate (PC3), cervical (HeLa), breast (HCC1806), colon (HCT116), lung (Calu-6), and pancreas (PANC1).
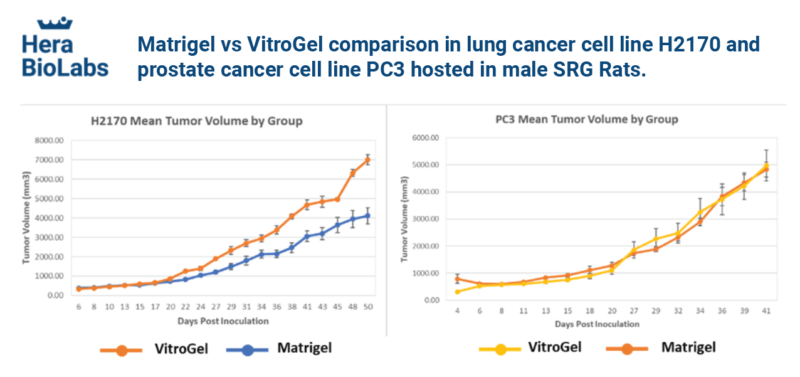
Matrigel vs VitroGel® comparison in lung cancer cell line H2170 and prostate cancer cell line PC3 hosted in male SRG Rats.
VitroGel® can support the growth of xenografted human lung and prostate cancer tissues at least as well as Matrigel in a rodent host with fast cell growth kinetics with low standard deviation.
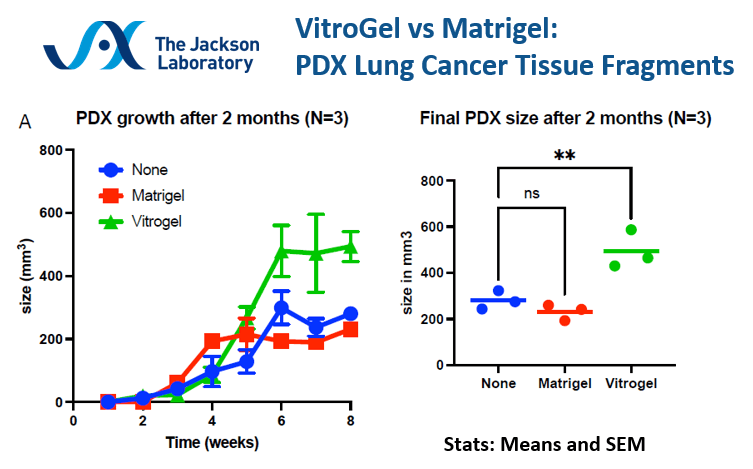
Matrigel vs VitroGel® comparison in PDX Lung Cancer Tissue Fragments.
VitroGel® shows better tumor growth and tumor size over Matrigel for PDX lung cancer tissue fragments. The PDX R&D Core at the Jackson Laboratory comments on the consistency and smooth operational use of VitroGel®, in addition to the mouse not showing darkening or bruising at the injection site as opposed to Matrigel.
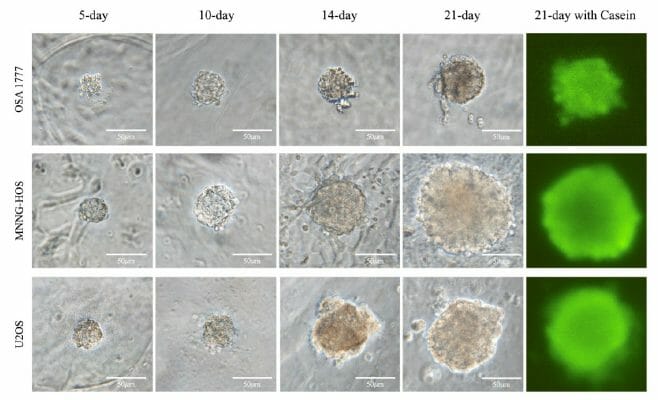
OSA 1777: A New Tool in the Fight Against Bone Cancer
Introducing OSA 1777, a cell line derived from recurring osteosarcoma, which unlike existing cell lines, forms spheroids in 3D culture reminiscent of osteosarcoma tumors.
RNF208, an estrogen-inducible E3 ligase, targets soluble Vimentin to suppress metastasis in triple-negative breast cancers.
Xenografting of triple-negative breast cancer cells into a mouse to test for tumor growth in response to the upregulation of a ubiquitin-related ligase protein.

Xenograft service
CDX or PDX models for Drug Discovery
With access to a large collection of tumor models,
connect with us for CDX, PDX, and Syngeneic tumor models.
Related publications Using VitroGel® in xenograft Application
- Tschon, M., Codispoti, G., Cabras, P., Cafarelli, A., Trucco, D., Vannozzi, L., Manferdini, C., Carniato, M., Cassiolas, G., Martini, L., Fini, M., D’Atri, G., Jost, C., Fedutik, Y., Nessim, G. D., Dumont, E., Lisignoli, G., & Ricotti, L. (2025). In Vivo Efficacy of an Injectable Piezoelectric Nanocomposite Hydrogel and Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound in Two Preclinical Models of Osteoarthritis.KeAi: Bioactive Materials https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.5128611
- Tsai, Y.-C., Kung Hung Cheng, Shih Sheng Jiang, Hawse, J. R., Shun En Chuang, Su Liang Chen, Huang, T.-S., & Hui-Ju Ch’ang. (2023). Krüppel-like factor 10 modulates stem cell phenotypes of pancreatic adenocarcinoma by transcriptionally regulating notch receptors. Journal of Biomedical Science, 30(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-023-00937-z
- Niwa, R., Hanamatsu, Y., Kito, Y., Saigo, C., & Takeuchi, T. (2022). Experimental model of micronodular thymic neoplasm with lymphoid stroma. Thoracic Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.14716
- Hakuno, S., Michiels, E., Kuhlemaijer, E., Rooman, I., Hawinkels, L., & Slingerland, M. (2022). Multicellular Modelling of Difficult-to-Treat Gastrointestinal Cancers: Current Possibilities and Challenges. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(6), 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063147
- Chen, Y., Zhang, X., Lu, X., Wu, H., Zhang, D., Zhu, B., & Huang, S. (2022). Ultra-sensitive responsive near-infrared fluorescent nitroreductase probe with strong specificity for imaging tumor and detecting the invasiveness of tumor cells. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 268, 120634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120634
- Arthur, P., Patel, N., Surapaneni, S. K., Mondal, A., Gebeyehu, A., Bagde, A., Kutlehria, S., Nottingham, E., & Singh, M. (2020). Targeting lung cancer stem cells using combination of Tel and Docetaxel liposomes in 3D cultures and tumor xenografts. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 115112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2020.115112
- Ramos, R. I., Bustos, M. A., Wu, J., Jones, P., Chang, S. C., Kiyohara, E., Tran, K., Zhang, X., Stern, S. L., Izraely, S., Sagi‐Assif, O., Witz, I. P., Davies, M. A., Mills, G. B., Kelly, D. F., Irie, R. F., & Hoon, D. S. B. (2020). Upregulation of cell surface GD3 ganglioside phenotype is associated with human melanoma brain metastasis. Molecular Oncology. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12702
- Kim, A.-Y., Yoon, Y. N., Leem, J., Lee, J.-Y., Jung, K.-Y., Kang, M., Ahn, J., Hwang, S.-G., Oh, J. S., & Kim, J.-S. (2020). MKI-1, a Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of MASTL, Exerts Antitumor and Radiosensitizer Activities Through PP2A Activation in Breast Cancer. Frontiers in Oncology, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.571601
- Weems, A. D., Welf, E. S., Driscoll, M. K., Mazloom-Farsibaf, H., Chang, B.-J., Weiss, B. G., Chi, J., Dean, K. M., Fiolka, R., & Danuser, G. (2021). Blebs Promote Cell Survival by Assembling Oncogenic Signaling Hubs. BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.23.441200
- Pang, K., Park, J., Ahn, S. G., Lee, J., Park, Y., Ooshima, A., Mizuno, S., Yamashita, S., Park, K.-S., Lee, S.-Y., Jeong, J., Ushijima, T., Yang, K.-M., & Kim, S.-J. (2019). RNF208, an estrogen-inducible E3 ligase, targets soluble Vimentin to suppress metastasis in triple-negative breast cancers. Nature Communications, 10(1), 5805. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13852-5