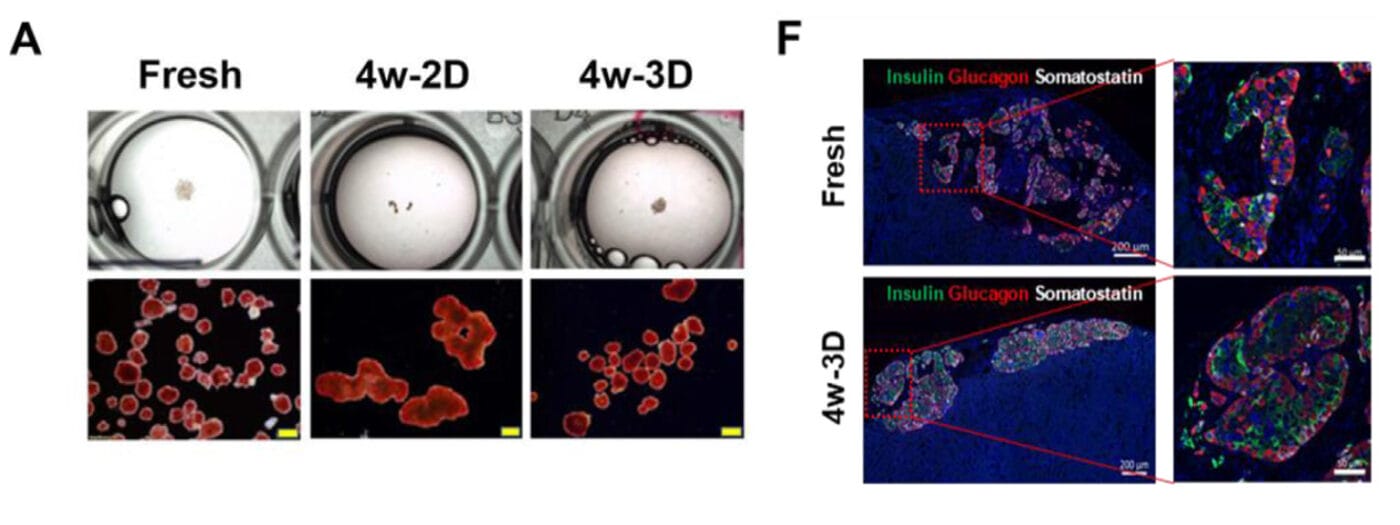
Institutions:City of Hope National Medical Center, CA Team:Omori, K., Qi, M., Salgado, M., et al., and Kandeel, F. Disease Model:Diabetes & Kidney Transplantation Hydrogel:VitroGel® 3D Human islet beta cells can be grown in 3D cell culture for up to eight weeks, rather than the three days they would survive in standard 2D culture. These cells […]
Author Archives: Eryka
Institutions:University of Graz, Austria Team:Zeiringer, S., Wiltschko, L., Glader, C., Reiser, M., Absenger-Novak, M., Frölich, E., & Roblegg, E. Disease Model:Intestinal Absorption Hydrogel:VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix Three hydrogels were tested as possible extracellular matrix mimics to establish a viable model of the human small intestine in the lab. The extracellular matrix, or ECM, is a network […]
Institutions:Rutgers University Team:Teryek, M., Jadhav, P., Bento, R., and Parekkadan, B. Disease Model:Liver & Kidney Failure Hydrogel:VitroGel® MSC Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be grown up to scale and genetically tuned for therapeutic deployment using a combination of a xeno-free hydrogel system and a vertical wheel bioreactor. In recent years we have been able to […]
Institutions:National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and National Institutes of Health (NIH), Maryland, USA Team:Babakhanova, G., Agrawal, A., Arora, D., Horenberg, A., Budhathoki, J.B., Dunkers, J.P., Chalfoun, J., Bajcsy, P., & Simon Jr., C.G. Disease Model:Tissue Repair Hydrogel:VitroGel® 3D The use of 3D optical coherence tomography (OCT) proves to be a quick, easy, and […]
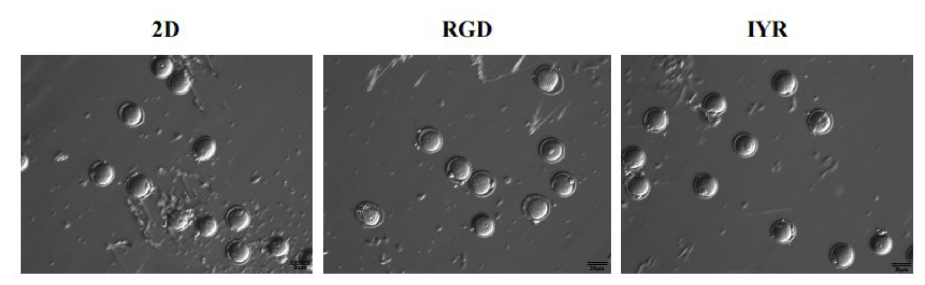
Institutions:Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University & University of British Columbia Team:Zhao, X., Zhang, S., Gao, S., Chang, H.-M., Leung, P.C.K., and Tan, J. Disease Model:Ovarian Cancer Hydrogel:VitroGel® RGD Three-dimensional cell culture in a hydrogel that was augmented with laminin peptides supports follicle tissue maintenance and hormonal function ex vivo. The human ovary contains an […]
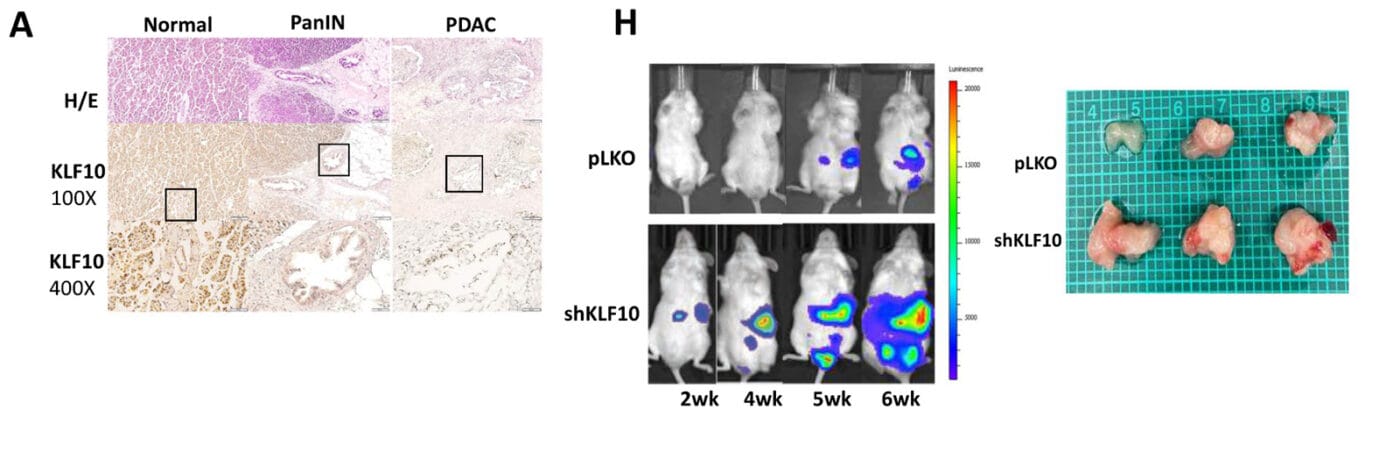
Institutions:Taipei Medical University, National Cheng Kung University, National Sun Yat-Sen University, and the National Institute of Cancer Research, Taiwan, and the Mayo Clinic. Team:Tsai, Y.-C., Cheng, K.H., Jiang, S.S., Hawse, J.R., Chuang, S.E., Chen, S.L., Huang, T.-S., and Ch’ang, H.-J. Disease Model:Pancreatic Cancer Hydrogel:VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix A mouse model for pancreatic cancer is developed that […]
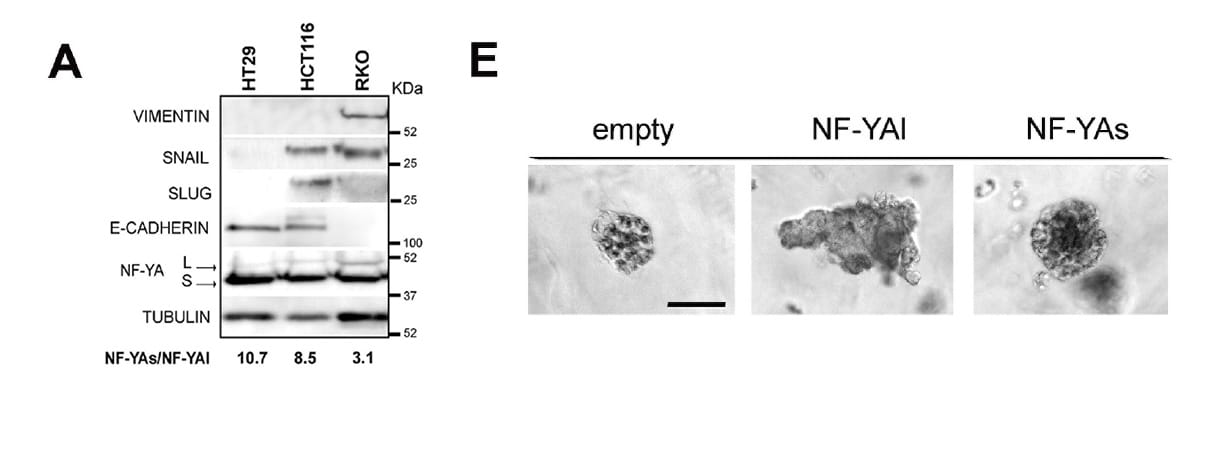
Institutions:University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, University of Milan, Italy Team:Rigillo, G., Belluti, S., Campani, V., Ragazzini, G., Ronzio, M., Miserocchi, G., Bighi, B., Cuoghi, L., Mularoni, V., Zappavigna, V., Dolfini, D., Mercatali, L., Alessandrini, A., and Imbriano, C. Disease Model:Colon Cancer Hydrogel:VitroGel® 3D A protein that binds DNA and can trigger colorectal cancer apparently […]
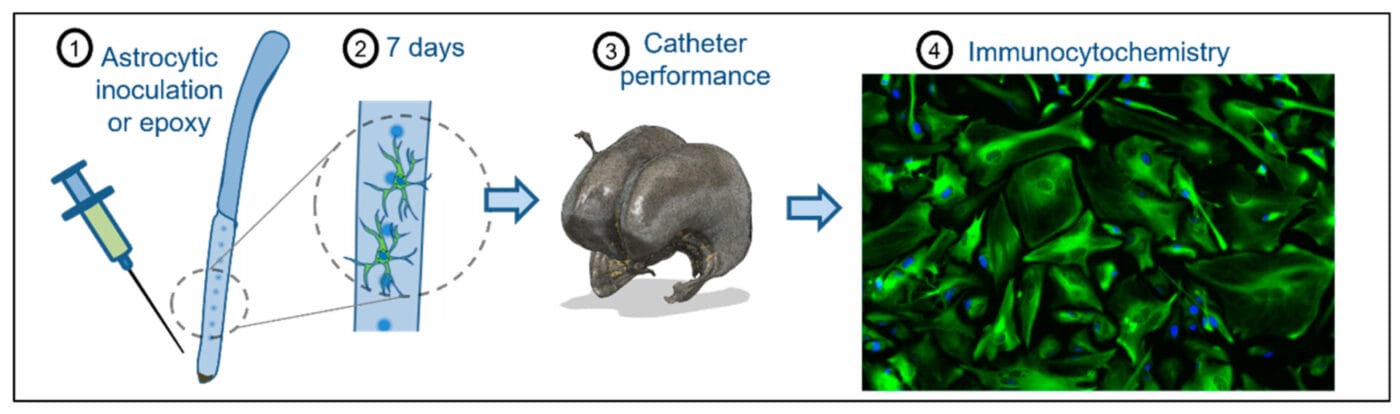
Catheters made from polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) turn out to be the most reliable in terms of not failing during the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid from children with hydrocephalus.
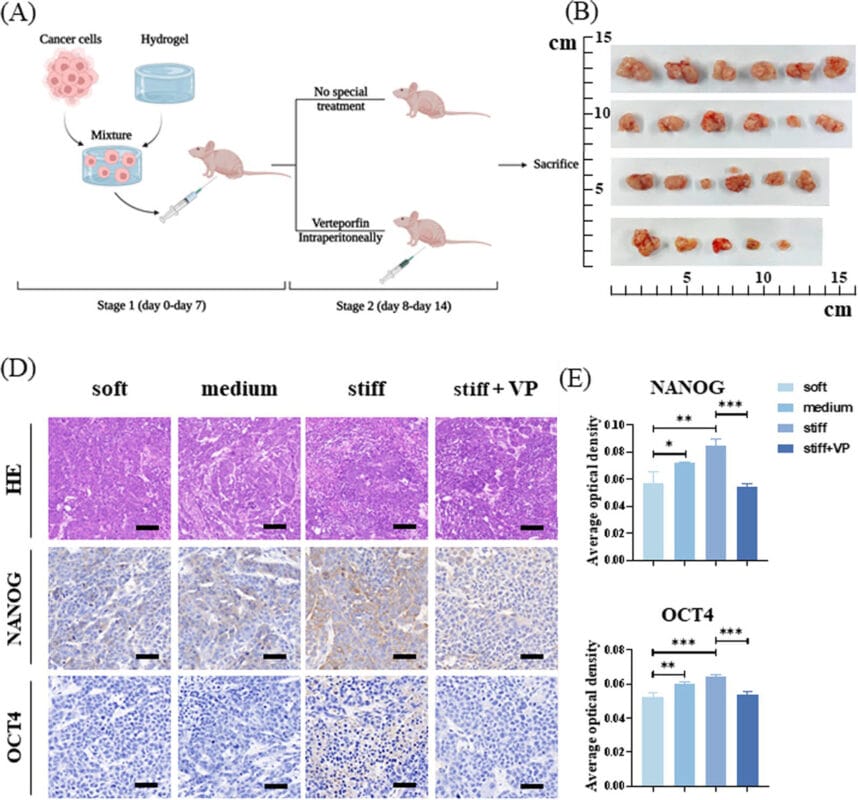
Institutions:Lanzhou University, China Team:Wei, J., Yao, J., Yang, C., Mao, Y., Zhu, D., Xie, Y., Liu, P., Yan, M., Ren, L., Lin, Y., Zheng, Q., & Li., X. Disease Model:Liver Cancer Hydrogel:VitroGel® 3D Cancer cell stiffness was measured by atomic force microscopy in tumors taken from liver cancer patients. The findings suggest that there are […]
Introduction Cell invasion is a dynamic process that is critical during embryonic development, immunosurveillance, and wound healing. Cell invasion is an orchestrated mechanism that occurs due to cell attachment to the extracellular matrix (ECM) followed by proteolytic degradation of the ECM, resulting in movement towards the newly invaded site. Cell invasion is not only crucial […]