Research Highlights
Harnessing Patient-Derived Organoids to Decode Immunotherapy Responses in Colorectal Cancer
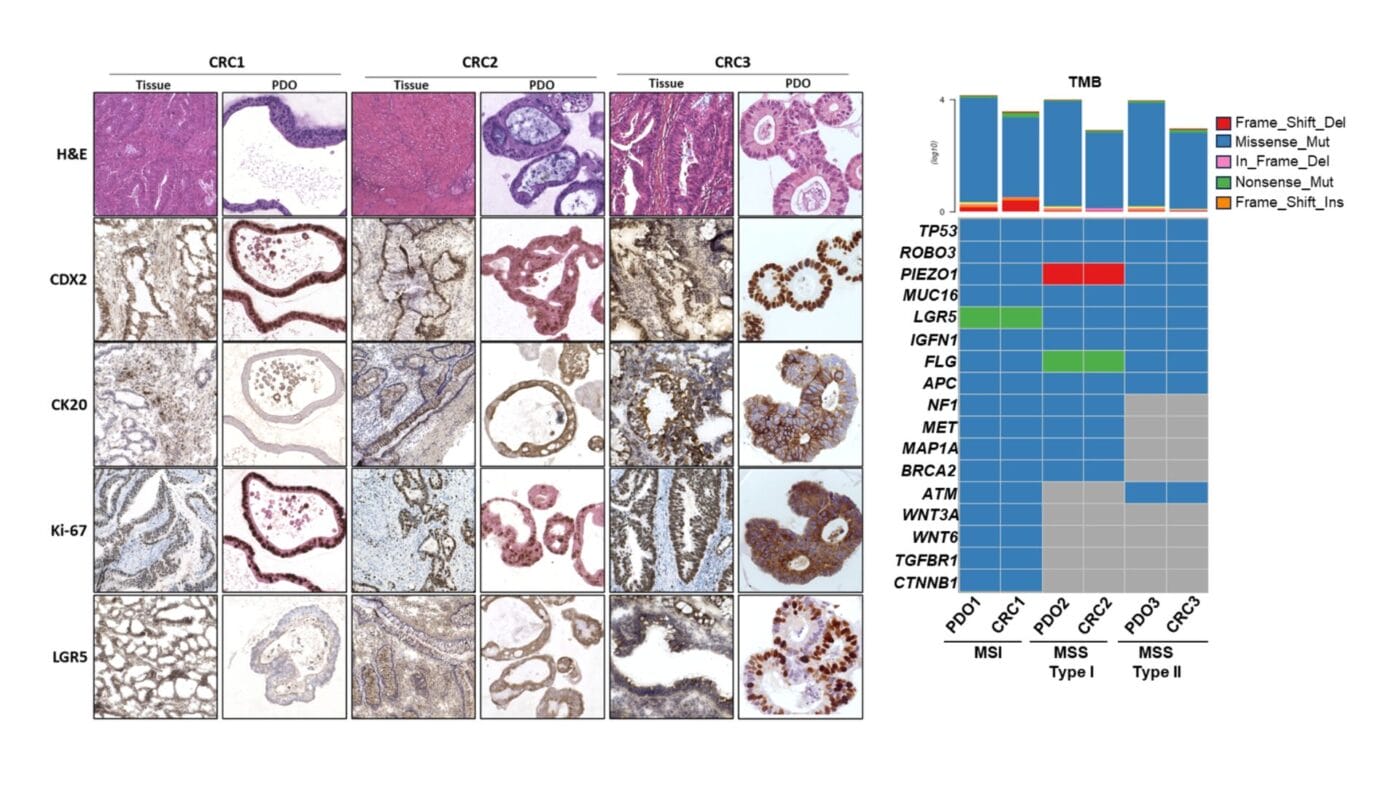
VitroGel® revolutionizes colorectal cancer research by creating a xeno-free platform for patient-derived organoids, enabling groundbreaking insights into tumor-immune interactions and immunotherapy responses.
Category:
Organoids
Subcategory/cell type:
Tissue Fragment/PDX – Organoid. Colorectal tumoral tissue
Institutions:
Fondazione Policlinico A. Gemelli IRCCS, Rome
Team:
Alice Dini, Harlan Carmine Carbone, Annachiara Esposito, Antonio Agostini, Giuseppe Quero, Geny Piro, Lorenzo Priori, Alessia Caggiano, Giulia Scaglione, Alessandra Battaglia, Maria Calegari, Lisa Salvatore, Maria Bensi, Maria Maratta, Anna Ceccarelli, Giovanni Trovato, Giannicola Genovese, Enrico Gurreri, Serena Ascrizzi, Maurizio Martini, Claudio Fiorillo, Andrea Fattorossi, Francesco De Sanctis, Stefano Ugel, Vincenzo Corbo, Sergio Alfieri, Giampaolo Tortora
Hydrogel:
VitroGel® MSC (Cat. No: VHM03)
Other VitroGel® option:
VitroGel® ORGANOID-3 (Cat. No: VHM04-3)
VitroGel® played a crucial role in establishing a patient-derived immunity-organoid interaction platform for colorectal cancer (CRC) research. By providing a xeno-free matrix for culturing patient-derived organoids (PDOs), VitroGel® enabled the precise integration of tumor and immune cell components, which is essential for studying the complex interactions within the tumor microenvironment (TME).
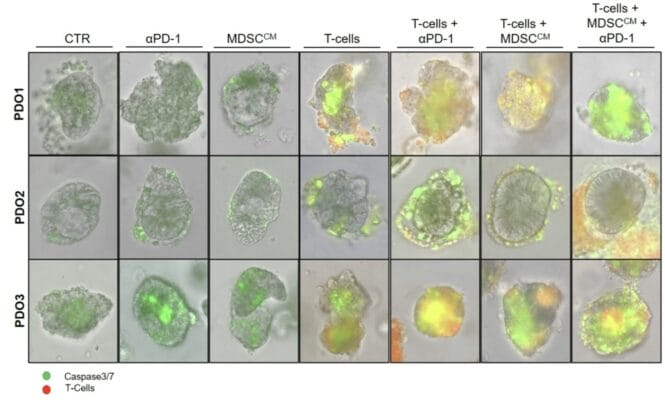
In this project, the organoids were cultured in VitroGel® , allowing researchers to simulate the natural conditions of the TME more accurately. This facilitated the co-culture of PDOs with autologous T-cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) conditioned media, enabling the exploration of how these components interact and influence responses to immunotherapy, such as pembrolizumab.
The use of VitroGel® helped maintain the integrity and functionality of the organoids, allowing for reliable assessments of T-cell activation and cytotoxicity in response to immunotherapy. Ultimately, this platform contributed to identifying potential markers of resistance to treatment, enhancing the understanding of immunotherapy responses in both microsatellite stable (MSS) and microsatellite unstable (MSI) CRC patients.